In this blog article, we show how deviceTRUST can be used to effectively administer all aspects of a Microsoft AppLocker configuration from within a single management console. We also show the methods that can be used to configure different platforms and how deviceTRUST can address the MDM interface in Windows 10 to enable offline capability and configuration without group policies.
A wide range of configuration options
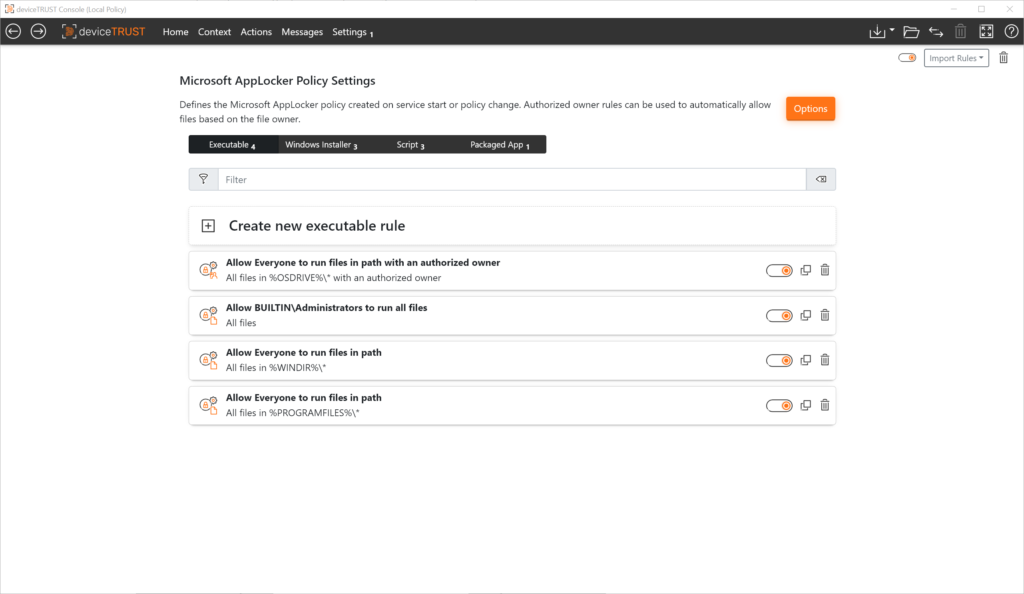
All aspects of Microsoft AppLocker configuration can be configured centrally from the deviceTRUST Console.
These include the following configuration options:
- Creation and management of all rules for executable files, Windows Installers, scripts and packaged apps including corresponding configuration wizards.
- Status of each file type (Disabled, Forced or Monitored)
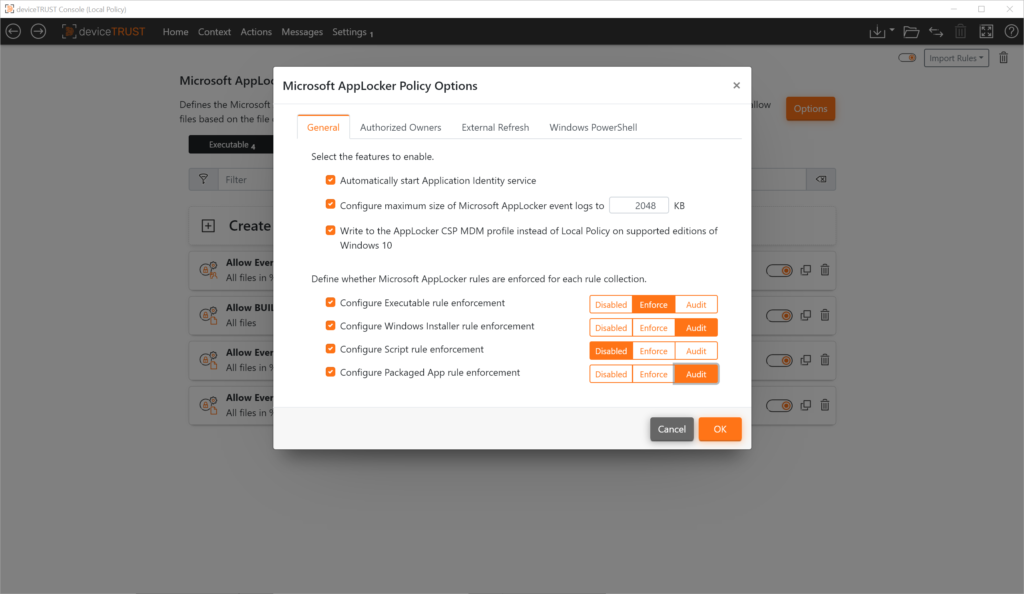
- Enable Microsoft AppLocker service (Application Identity service)
- Defining the maximum size of the Microsoft AppLocker event log
- Defining the Microsoft AppLocker interface to use (local policy or AppLocker MDM interface)
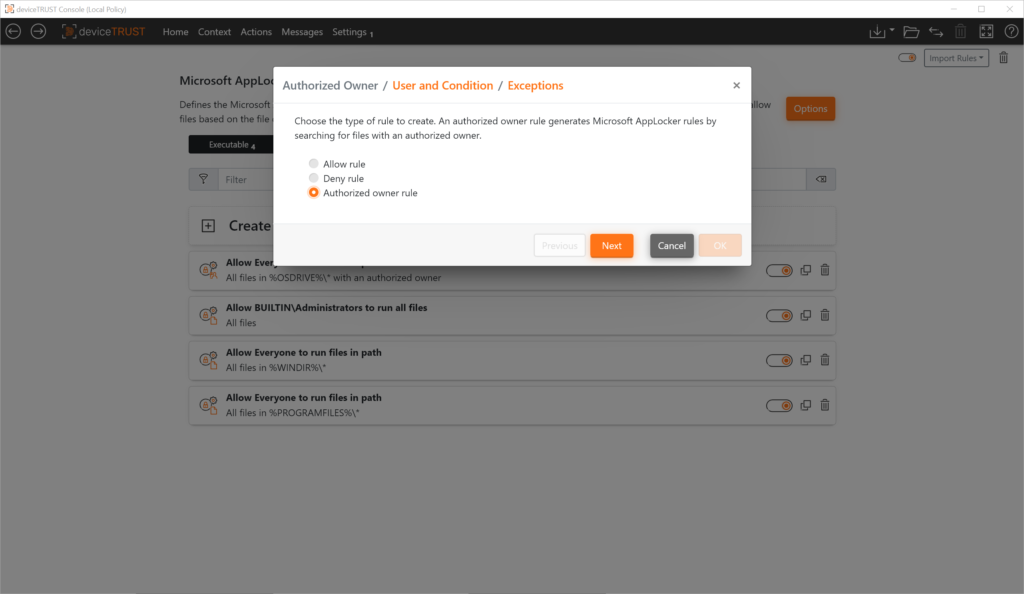
- Defining the “Authorized Owner” for automated creation of the application allow lists including folder exceptions
- Control the ability to update the Microsoft AppLocker policy by an administrative user at runtime
- Microsoft PowerShell extension to prevent the use of unknown PowerShell scripts and commands
For the creation of rules for executables, Windows Installers, scripts and packaged apps, new options are available with deviceTRUST in addition to the familiar AppLocker methods. These greatly simplify the creation of an application allow lists, for example, and automate the process as far as possible.
- The “Authorized Owner” principle enables the automated creation of a allow lists based on the NTFS property “Owner”.
- The extension of AppLocker variables to standard environment variables makes the creation of the ruleset more flexible.
Deployment Methods
After a Microsoft AppLocker configuration is created in the deviceTRUST Console, the deviceTRUST policy must be deployed to the target systems and enabled. Depending on how the target systems are managed, you can choose between two deployment options for the deviceTRUST Policy:
Microsoft Group Policy Management (GPO)
The deviceTRUST Console integrates seamlessly with the Group Policy Management console. All policies created in the deviceTRUST Console are stored within the loaded Group Policy. The Group Policy, including the deviceTRUST Policy, is deployed and activated to the target systems using familiar Microsoft Group Policy methods.
The deviceTRUST Agent on the target system reads the Group Policy with the included deviceTRUST Policy and activates the AppLocker configuration. If the Group Policy is removed, the deviceTRUST Policy is also completely removed from the target system and all Microsoft AppLocker configurations are reset.
Management via GPO does not require any customization to Active Directory. Also, no ADMX templates need to be imported.
File-based Configuration
File-based configuration writes the deviceTRUST Policy from the deviceTRUST Console to a deviceTRUST Configuration File. This configuration file must be copied to a defined folder on the target system. There it is read and activated by the deviceTRUST Agent. By default, all administrative users can place or delete the deviceTRUST Configuration Files in the appropriate folder. The authorized group can also be restricted in the deviceTRUST Console.
Hybrid Configuration
In some deployment scenarios, it makes sense to combine the deployment option. In this case, the different configurations from the various sources are merged on the target system.
Interfaces
Regardless of the deployment method used, the Microsoft AppLocker configuration is activated by deviceTRUST when the target system boots and a deviceTRUST policy is present. This is done using either the Local Computer Policy (Windows Server operating systems and supported Windows 10) or the Windows MDM interface (Windows 10 Professional, Windows 10 Enterprise).
Summary
Whether Microsoft AppLocker is to be used for classic notebooks managed via Microsoft Active Directory (AD), on enterprise notebooks connected to Microsoft Azure Active Directory (AAD), in local remoting environments or in DaaS environments, deviceTRUST makes it very easy to centrally create, deploy and manage all appropriate AppLocker configurations!
In the next blog article, we will show how the required application allow lists for Microsoft AppLocker can be created very easily in an automated way. For this purpose, we will use new technologies such as the “Authorized Owner” principle to automatically detect and release allowed applications and block unknown applications.
If you want to learn more, make an appointment with our technical experts!